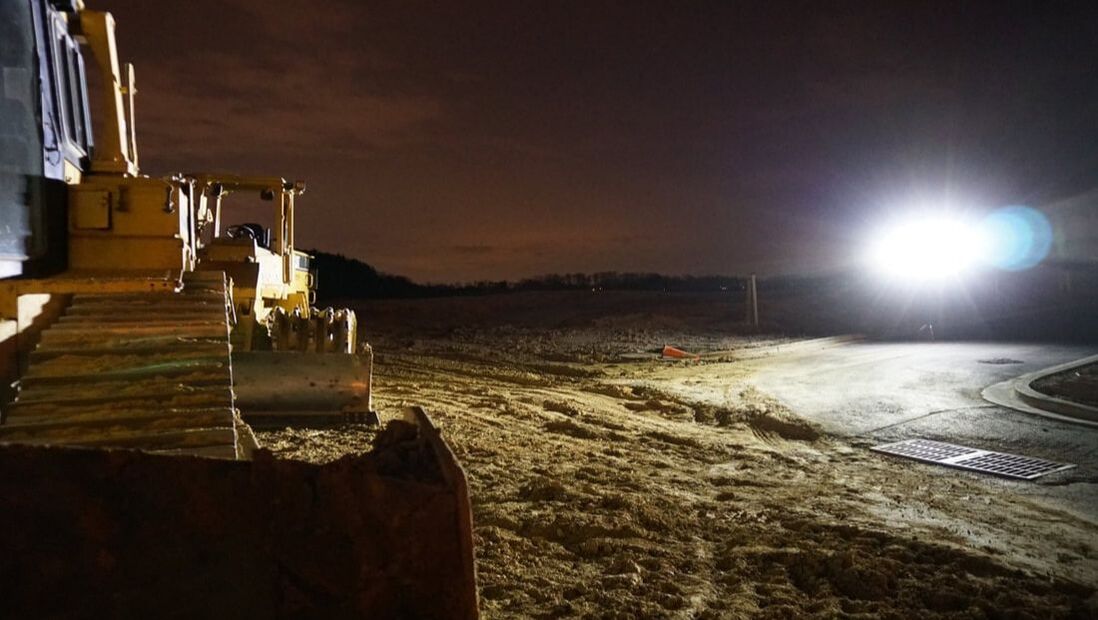
What are LEDs?LED: (short for Light Emitting Diode) are gradually phasing out all other types of lighting. Among the hype for LED lights are the claims that they are more effective, stemming from their balance brightness, lifespan, durability, and efficiency. Compared to an incandescent or CFL bulb, an LED will last much longer on average with a superior quality. From the Candle to the Lightbulb Typical lights, such as incandescent, CFL, or halogen lights, have a lot in common with how a candle produces light – they burn stuff. Whether purely through burning a filament or by generating heat to excite an inert gas (mercury vapor for CFLs, iodine and bromine for halogens), older lightbulbs took the age-old concept of the candlelight and adopted it to work with electricity. While this has its inherent tradeoffs of heat expenditure and decreased lifespan, for all intents and purposes it was revolutionary. Are LEDs Dangerous?Blue Light and Sleep Primarily, the dangers of blue light lie in its conflict with our circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is the biological process driving our sleep cycles. Blue light is good for stimulation during the day and keeping us alert; therefore, exposure to large amounts of blue light during nighttime disrupts the circadian rhythm, causing sleep to suffer. While researchers have suggested a link between excessive blue light exposure to types of cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and obesity, organizations such as Harvard Medical School highlight that these results are “not proof that nighttime light exposure causes these conditions.” [1] Regardless, getting a good night’s sleep is important; thus, it is paramount we exercise caution and minimize our blue light exposure. Minimizing Blue Light Exposure There are several solutions to the problem of blue light exposure; major tech companies such as Apple have already applied methods including shift to red light in the night and morning to mitigate any ill consequences. Among some steps you can take yourself:
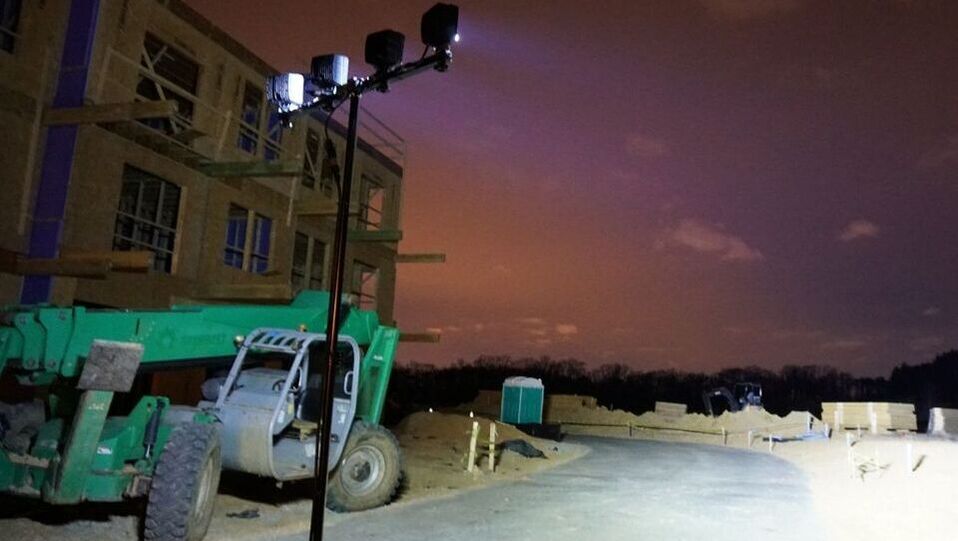
[1] https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/blue-light-has-a-dark-side LEDs vs. Halogen Lights. What's The Difference?Halogen lights have largely seen a decline in the 21st century. Growing out of solutions that combined incandescent and compact fluorescent light with halogens from the periodic table, such as iodine and chlorine to keep the bulbs clear, they’re being actively phased out by LED lighting. Why is that? Halogen lights work by preventing tungsten, an element evaporating from bulbs, from accumulating on the bulb’s exterior. The halogens cause a reversible reaction by combining with the tungsten to form compounds such as tungsten iodide, which do not adhere to the bulb walls. The major problem with halogen lights is that they eat up a lot of energy – and they’re hot. In order to maintain the halogen reaction with tungsten, the bulb must operate above 250 degrees Celsius, sometimes even reaching temperatures of 540 degrees. A lot of energy is lost to heat. This not only drives energy costs up – it creates a prominent fire hazard. LED lamps, or light emitting diodes, offer an even greater quality of light and only use about 10% of the energy incandescent bulbs do [1]. Compared to halogen lamps, the savings are even more profound. LEDs can operate much longer and more reliably than halogen, incandescent, or CFL lights. Generating less heat, they are safer alternatives that reduce the amount of energy required for a similar lumen output. A halogen lamp has a distinct advantage over CFL and incandescent lights in terms of a longer life span, some ranging up to 15,000 hours. The LED, however, has evolved past the halogen lamp, reaching upwards of 25,000 hours. Being a safer, cheaper, and longer-lasting solution, LED lamps are the way of the future. 3 Types of LED Construction LightingLED Spotlights Spotlights focus all their power onto a small area to provide you the highest amount of brightness possible; they are intended for single target applications. When performing a task where the ability to see clearly is paramount in a small working area, spotlights are the best choice. When working in a confined area intensively, spotlights are a necessary asset to ensure the job is done right at times or in locations where natural light is scarce. LED Floodlights Floodlights canvas a large area with high throw distance, spread, and great luminosity. While they will not provide the same brightness as a spotlight on a specific object, they will raise the visibility of an entire area on a jobsite. In the area of operations, floodlights are critical to ensuring your safety and the safety of your workers. To ensure the entirety of your workplace can be seen, especially areas where movement of materials and people are prevalent, floodlights are a necessary element. LED Hybrid Lights Hybrid lights combine the best of both worlds, giving users the opportunity to utilize spotlight capabilities to highlight specific objects or a floodlight option over a widespread area. For multiheaded lights, such as adjustable quad lights, hybrid lights are excellent to perform tasks with precision while providing protection about the vicinity. For workers whose work takes place in the middle of a dynamic area, hybrid lights are a tool to keep them safe, both from their surroundings and in their engagement in work. The Future of LED LightingWhite OLEDs White OLEDs, also known as White Organic Light-Emitting Devices, are a hot topic for research in applications of solid-state lighting. Researchers are currently working to convert the revolutionary LED technology sweeping the computer, TV, and smartphone display markets to your household. What makes OLEDs touted as the LEDs of the near future? Unlike typical multi-color LED displays that rely on LCD, or liquid crystal displays, OLEDs do not require a backlight – they make their own visible light when exposed to an electrical current through a layer of organic compound. This allows for a greater range of color and contrast, as well as power efficiency, compared to traditional LED solutions. In addition, it is presumed that the technology will become cheaper to produce than typical LEDs as OLED components, known as OLED substrate, can be printed onto materials. microLEDs microLEDs, like white OLEDs, are an emerging technology; unlike white OLEDs which are specifically targeting solid-state applications, microLEDs are currently in the phase of research and development for smaller power use devices. It may be a while until we fully see them in lighting applications outside of displays for devices; however, there are bountiful benefits which hold much promise for microLED technologies as the wave of the future. Whereas OLEDs operate off organic material, microLEDs are based on gallium nitride; gallium nitride offers far greater brightness than its OLED counterparts while touting higher energy efficiency, and a longer average lifespan. Aside from its energy efficiency, microLEDs promise greater contrast and quicker response times to their LCD and OLED counterparts. Choose SiteLitesIf you want to cut costs while safely lighting up your space, you should look to a company experienced with LED solutions. SiteLites specializes in lighting solutions with our family of LED work lights designed around customer safety. SiteLites's expertise with power management solutions is a critical aspect of ensuring your LED performance. LED’s, while operating at low heat, are sensitive to exposure. SiteLites has implemented solutions such as cast-aluminum heat sinks and adaptive power prioritization that will keep your bulbs running. Related Articles
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
October 2020
Categories |
Very Bright!Located in Pinellas Park, FL, SiteLites has been providing bright, temporary work lighting to keep jobsites safe. Let us help you work safer for longer!
Follow Us3845 Gateway Centre Blvd.
Suite 360 Pinellas Park FL 33782 |
Quick LinksLighting Solutions1.8K Lumen Magnetic Lantern
6K Lumen Floor Light 9K Lumen Mono Tripod Light 12K Lumen Quad Tripod Light How We Can Help |
|














 RSS Feed
RSS Feed




